
Root Cause Analysis
October 7, 2024
Colleague in the Spotlight – Brent
October 24, 2024Quality Control (QC) is the department which ensures that the incoming materials, products, utilities and cleanrooms are of sufficient quality for their use. The importance of QC stems from the undeniable obligation to deliver quality product that guarantees patient safety. Therefore, the need of a QC department has been made compulsory by several regulations including the EudraLex’s guidelines for GMP and FDA’s 21 CFR.
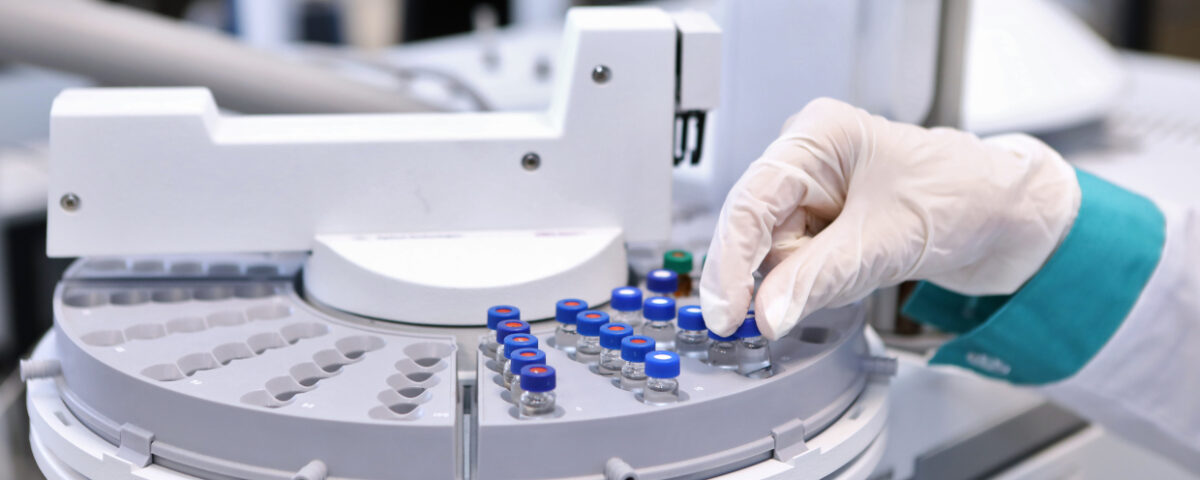
As the name suggests, the quality of incoming material, products, cleanrooms and utilities is verified in the QC labs. The specification to which the test materials comply are based on regulation and scientific rational. The cleanrooms for example have specifications based on regulation. To control whether the different specifications are met, QC will take samples and test the specifications. The same idea works for the incoming materials, (intermediate) products and utilities.
But quality control goes beyond simply controlling quality. Its responsibilities span across a range of critical activities, such as:
- Sampling, Testing, and Analysis: Systematic sampling and rigorous testing ensure that every product and material complies with specifications.
- Instrument Calibration: Regular calibration of lab instruments ensures the accuracy and reliability of test results.
- Data Recording and Documentation: Accurate and detailed record-keeping of test results, procedures and observation records is essential for traceability, accountability and regulatory compliance.
- Review and Interpretation: QC teams review and interpret test results, ensuring data is conform with the specifications and standards.
- OOS (Out of Specification) Investigations: Identifying and addressing any deviations from quality standards ensures that nonconformities are swiftly resolved.
- Document Review: Thorough documentation review guarantees all processes align with regulatory requirements.
- Release or Rejection of Products: Based on testing outcomes, QC determines whether raw materials and products are ready for release or should be rejected.
- Continuous Improvement: QC continuously evaluates processes to enhance efficiency and accuracy, driving long-term improvements in product quality.
Through these varied responsibilities, QC labs ensure that every product not only meets regulatory standards but also consistently delivers on safety and quality. This comprehensive approach—from testing and analysis to continuous improvement—plays a pivotal role in safeguarding public health and maintaining industry trust.
Ultimately, QC’s work underpins the delivery of high-quality products that patients can rely on.




1 Comment
[…] fact, when there is a deviation from the validated procedure, a deviation will be started in our system. This event must then be investigated with the aim of identifying a […]